types of vaccine delivery system
This type of vaccine introduces a safe modified version of the virus known as the vector to deliver genetic code for the antigen. Cancer vaccines are the promising tools in the hands of the clinical oncologist.
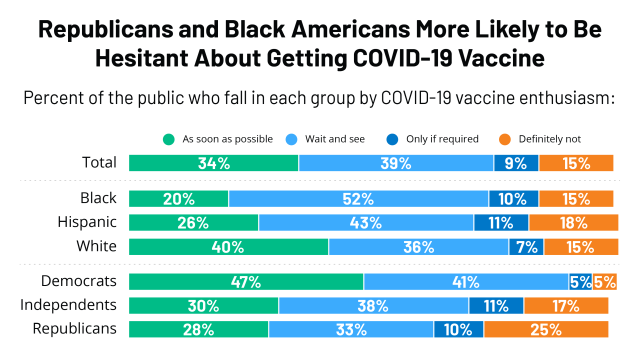
Kff Covid 19 Vaccine Monitor December 2020 Kff
Vaccines Subunit administration dosage.

. Adjuvants Immunologic administration dosage. Techniques such as sonophoresis microneedle-assisted delivery iontophoresis and elastic liposomes are among those being used and developed for transdermal vaccine delivery. Messenger RNA mRNA vaccine.
Many tumor-associated antigens are excellent targets for immune therapy and vaccine design. Recommended Childhood ages 0-6 Immunization Schedule. In a COVID-19 vaccine the vector is the spike proteins found on the surface of the coronavirus.
Vaccines based on messenger RNA mRNA an intermediary between DNA and protein also are being developed. Other licensed vaccines that use this type of technology. Delivery systems for mRNA vaccines can be divided into viral- and non-viral vector delivery systems.
Vaccines are the preparations given to patients to evoke immune responses leading to the production of antibodies humoral or cell-mediated. Live attenuated vaccines fight viruses and bacteria. The size of the particle systems influences cellular targeting.
Or being studied include. Polio IPV Hepatitis A. Antibody Formation drug effects.
The weakened virus viral vector serves as a delivery system. Optimally designed cancer vaccines should combine the best tumor antigens with the most effective immunotherapy agents andor delivery strategies to achieve positive clinical results. Recent trends in vaccine delivery systems.
Viral vectored vaccines are significantly cheaper to produce in most cases compared to nucleic acid vaccines and many subunit vaccines. New developments in vaccine delivery systems will improve the efficiency of clinical trials in the near future. Concerted efforts by researchers on alternative vaccine delivery routes have yielded a range of novel delivery devices with potential to enhance immunogenicity and stability.
We will discuss each of these briefly in the following slides. Ni-NCs were characterized for binding His-tagged model proteins through high-affinity non-covalent interactions. Among them nanoparticles NPs such as dendrimers polymeric NPs metallic NPs magnetic NPs and quantum dots have emerged as effective vaccine adjuvants for infectious diseases and cancer therapy.
Children should return to full-time in-person learning in the fall. In particular they describe novel polymeric. Examples of vaccine delivery systems include liposomes emulsions and microparticles.
In this Special Focus experts in the field describe recent innovations in the design evaluation and use of novel vaccine delivery devices and systems. Improving current delivery methods or designing new ones can enhance the use of existing medications. Drug Delivery Systems methods.
CDC recommends universal indoor masking for all teachers staff students and visitors to K-12 schools regardless of vaccination status. Sonophoresis is a technique that uses ultrasound to permeabilize the stratum corneum layer of the skin. In this type of vaccine genetic material from the COVID-19 virus is inserted into a different kind of weakened live virus such as an adenovirus.
The vaccine delivery options available may also differ geographically. Vaccines of this type on US. The purpose of this study was to design novel nanocapsules NCs with surface-chelated nickel Ni-NCs as a vaccine delivery system for histidine His-tagged protein antigens.
The vaccine or drug is generally placed in or on the microneedle tip. The main types of COVID-19 vaccines currently available in the US. Antibody Formation immunology.
Drug Delivery Systems trends. A vaccine typically contains an agent that resembles a disease-causing microorganism and is often made from weakened or killed forms of the microbe its toxins or one of its surface proteinsThe agent stimulates the bodys immune system to recognize the agent. Vaccines Subunit immunology.
Described as a hybrid between a hypodermic needle and a transdermal patch microneedles are tiny needles less than 1mm made of polymer metal silicon glass or ceramic. The common routes of vaccine delivery are parenteral injection needle-free injections intranasal ocular oral and spray topical. Vaccine suspension of weakened killed or fragmented microorganisms or toxins or other biological preparation such as those consisting of antibodies lymphocytes or messenger RNA mRNA that is administered primarily to prevent disease.
For example NIAID-supported researchers developed. Microneedle arrays are one example of a new method to deliver medications through the skin. Measles mumps rubella MMR combined vaccine Varicella chickenpox Influenza nasal spray Rotavirus.
Miniaturizing the vaccine delivery system also reduces the burden on the so-called cold chain a baton race from manufacturing plant to patient arm through a series of special refrigerated trucks and shipping containers designed to keep vaccines at. These vaccines contain a version of the living virus or bacteria that has been weakened so that it does not cause serious disease in people with. Most vaccine delivery systems are particulate including nanoparticles microparticles or adjuvant-formulated proteins.
After vaccination your muscle cells begin making the S protein. Toxoid inactivated toxin Diphtheria tetanus part of DTaP combined immunization. Given new evidence on the B16172 Delta variant CDC has updated the guidance for fully vaccinated people.
Dime-sized patch of dissolvable microneedles for self-administration of influenza vaccine. Recent technological advances have largely overcome issues with the instability of mRNA and the difficulty of delivering it into cells and some mRNA vaccines have demonstrated encouraging early results. Today there are five main types of vaccines that infants and young children commonly receive in the US.
This photo shows a r esponder at an. This review mainly discusses non-viral vectors which can be further subdivided into lipid or lipid materials and polymer delivery systems. Replicating Replicating viral vectors retain the ability to make new viral particles alongside delivering the vaccine antigen when used as a.
Both the Pfizer-BioNTech and the Moderna COVID-19 vaccines use mRNA. This type of vaccine uses genetically engineered mRNA to give your cells instructions for how to make the S protein found on the surface of the COVID-19 virus. A vaccine is a biological preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious disease.
Anywhere from one to thousands of needles are fixed to a baseplate or backing layer.

Intranasal Covid 19 Vaccines From Bench To Bed Ebiomedicine
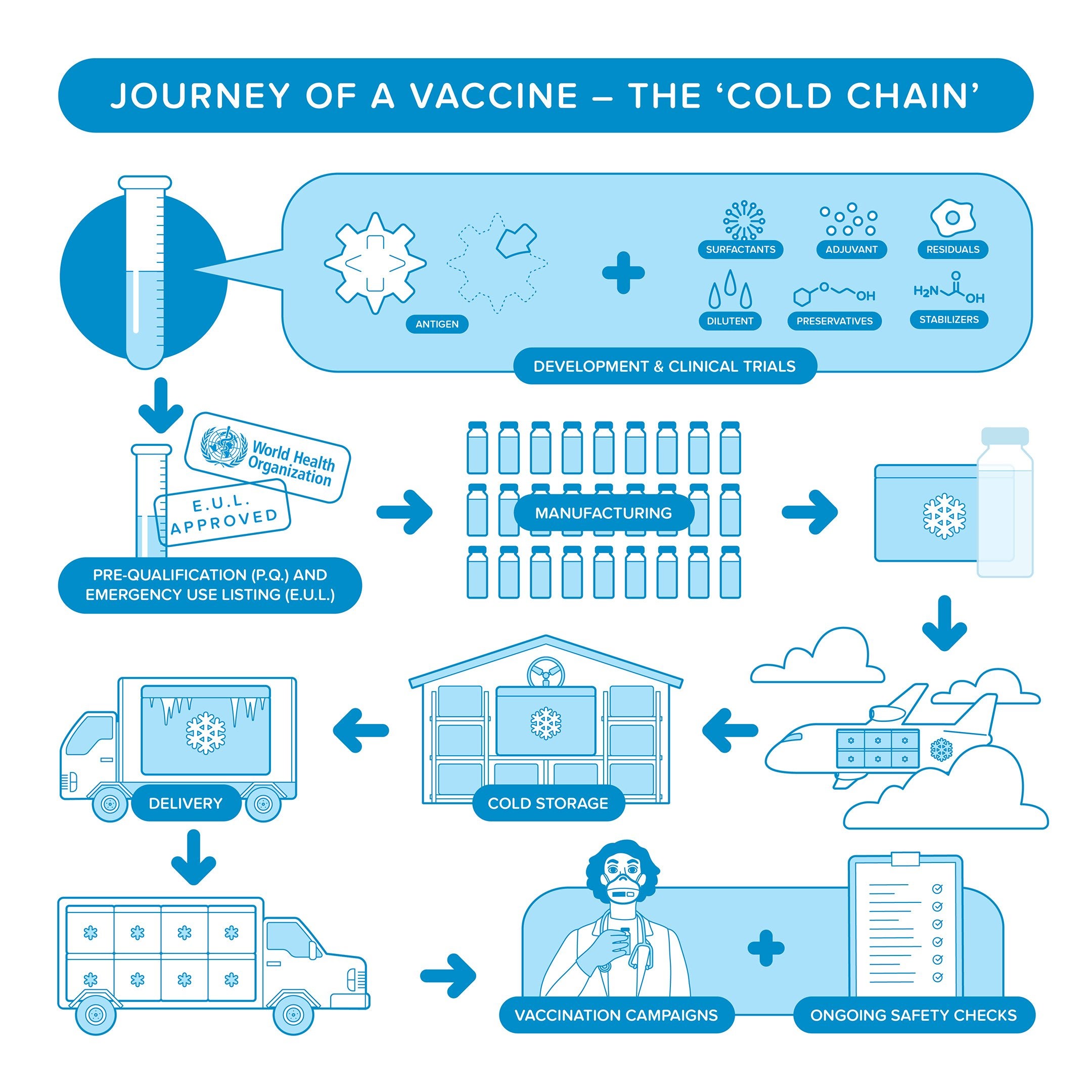
Cold Chain Paho Who Pan American Health Organization

Forward Of Targeted Drug Delivery Jmdh Jmdh
How Pfizer S Mrna Coronavirus Vaccine Compares To Other Us Candidates
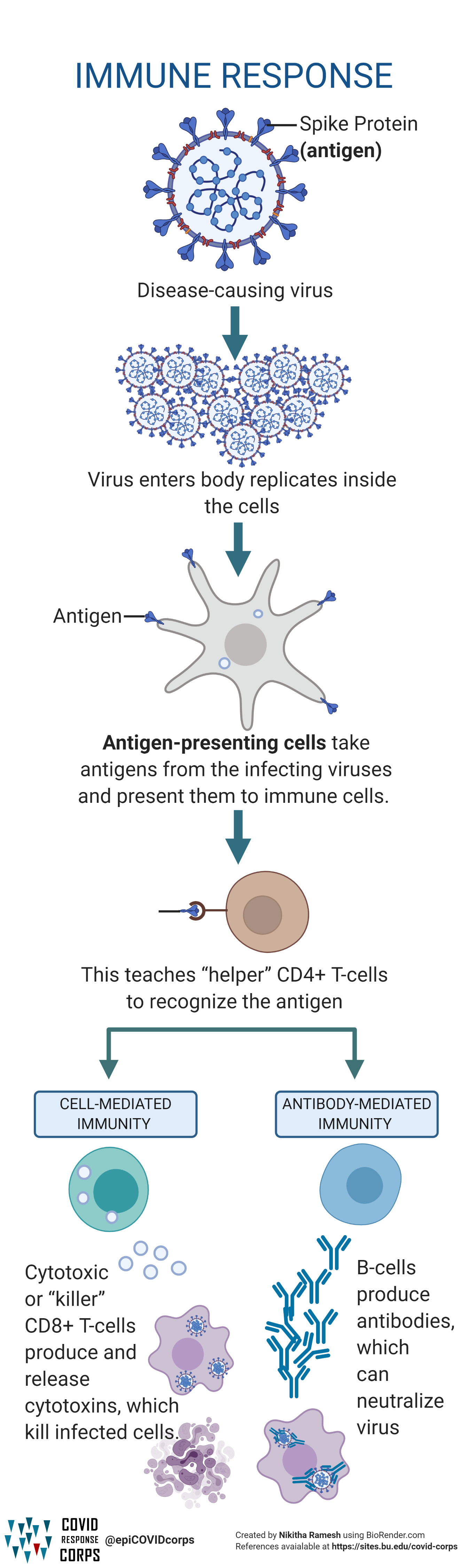
Types Of Vaccines Infographics Epidemiology Covid 19 Response Corps

How The Sinovac Covid 19 Vaccine Works The New York Times
Covid 19 Vaccine Brand Hesitancy And Other Challenges To Vaccination In The Philippines

States Are Getting Ready To Distribute Covid 19 Vaccines What Do Their Plans Tell Us So Far Kff
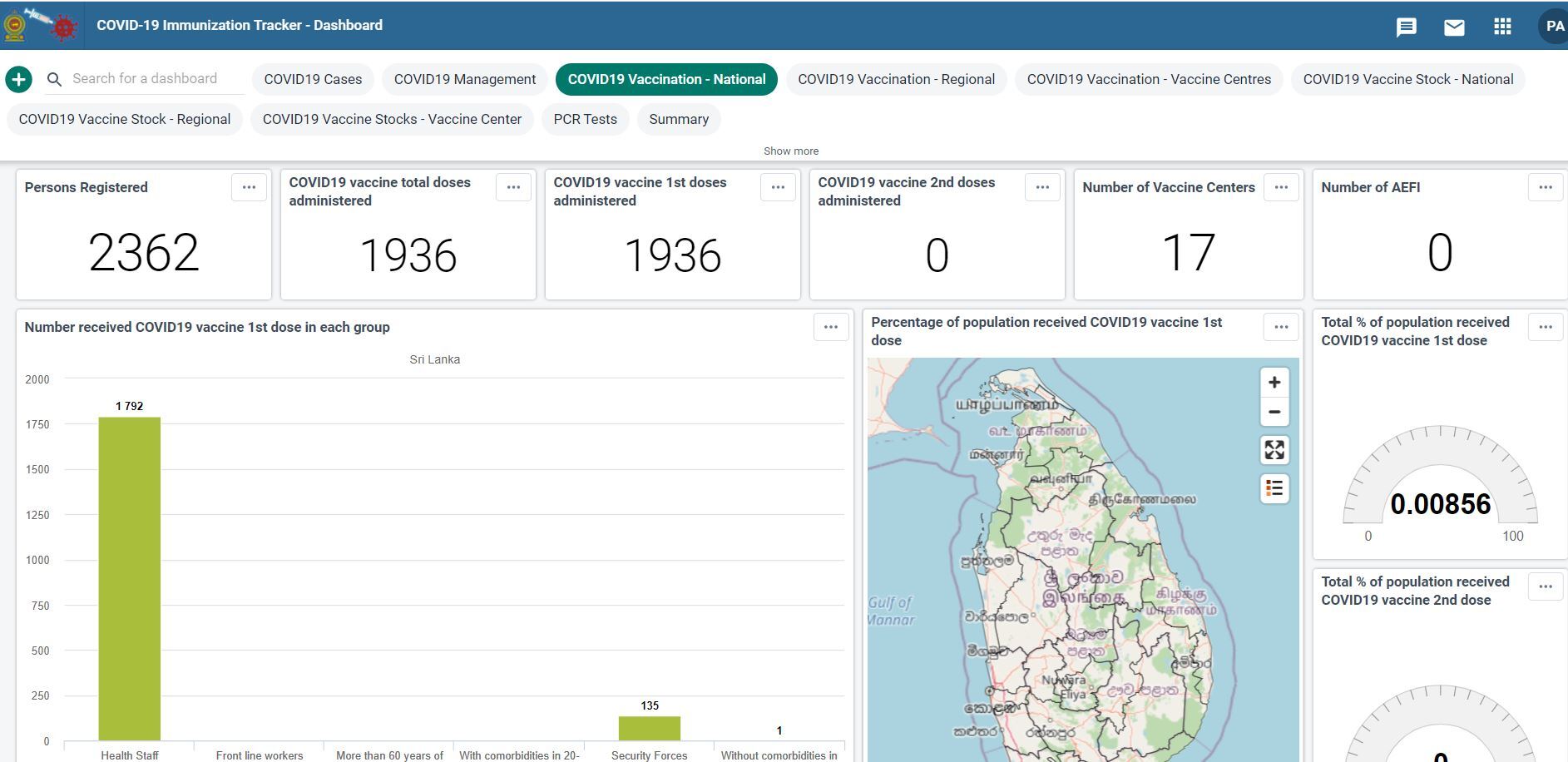
Innovative Management Of Covid 19 Vaccine Delivery In Sri Lanka Dhis2

Current And Future Nanoparticle Vaccines For Covid 19 Ebiomedicine

Coronavirus And The Covid 19 Vaccine Health Mil

Intranasal Covid 19 Vaccines From Bench To Bed Ebiomedicine
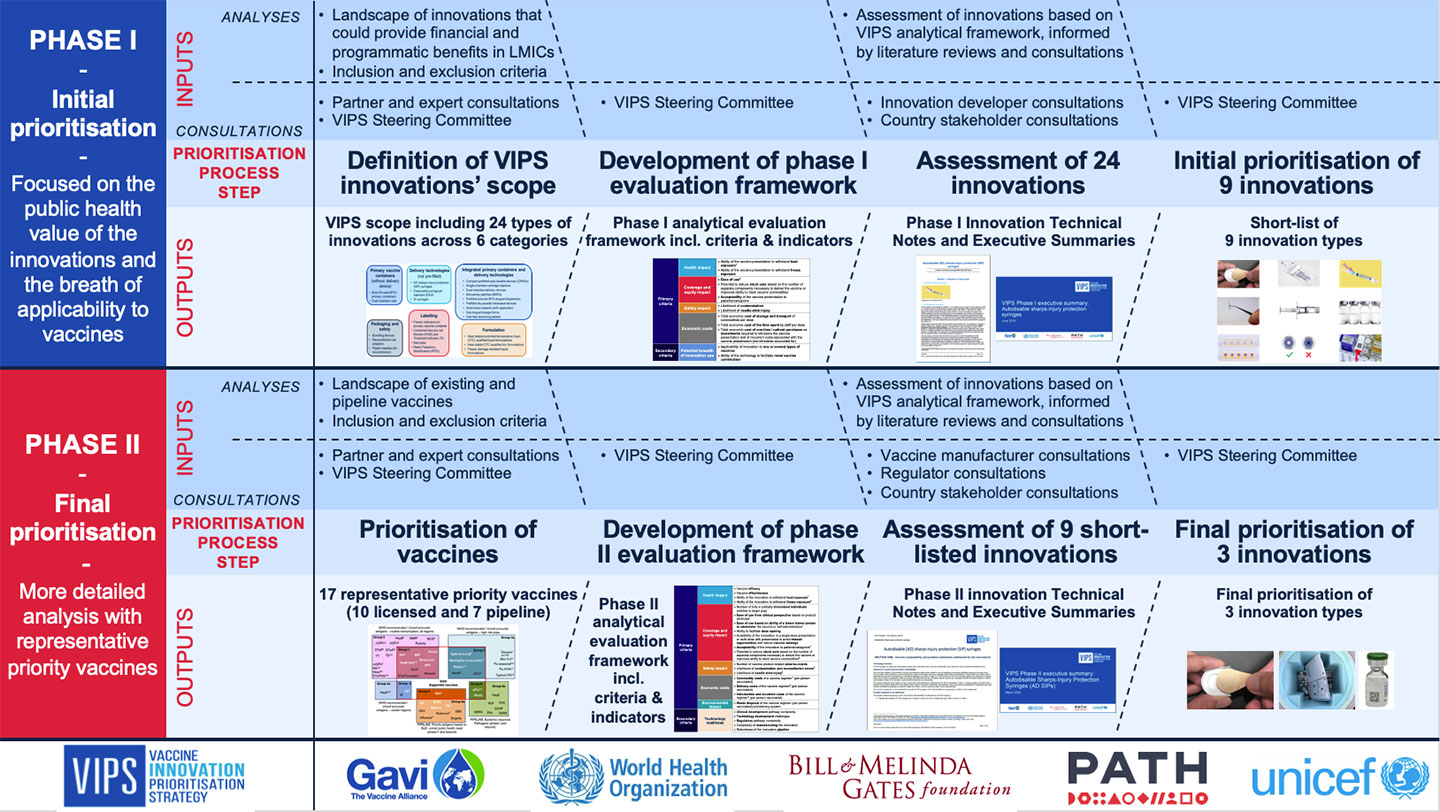
The Vaccine Innovation Prioritisation Strategy

Covid 19 Vaccines For Homebound Patients And Their Caregivers Catalyst Non Issue Content
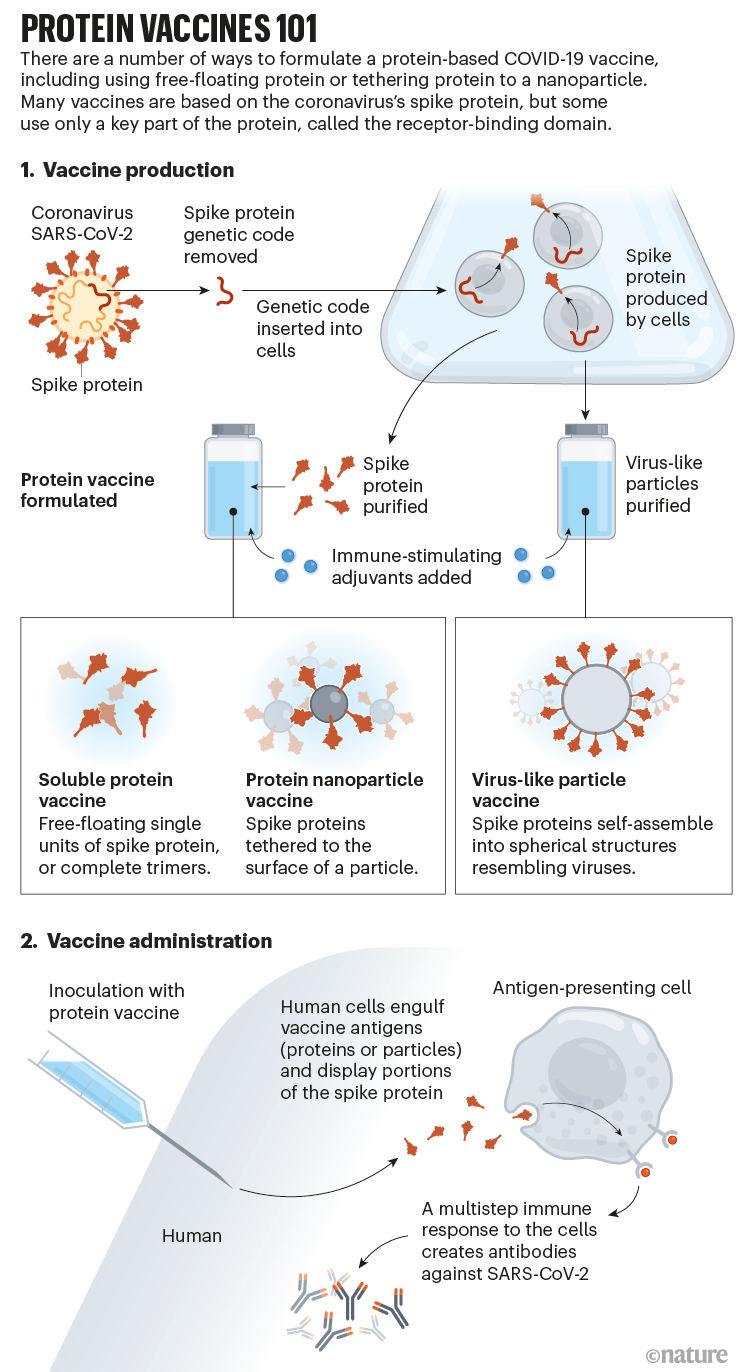
How Protein Based Covid Vaccines Could Change The Pandemic
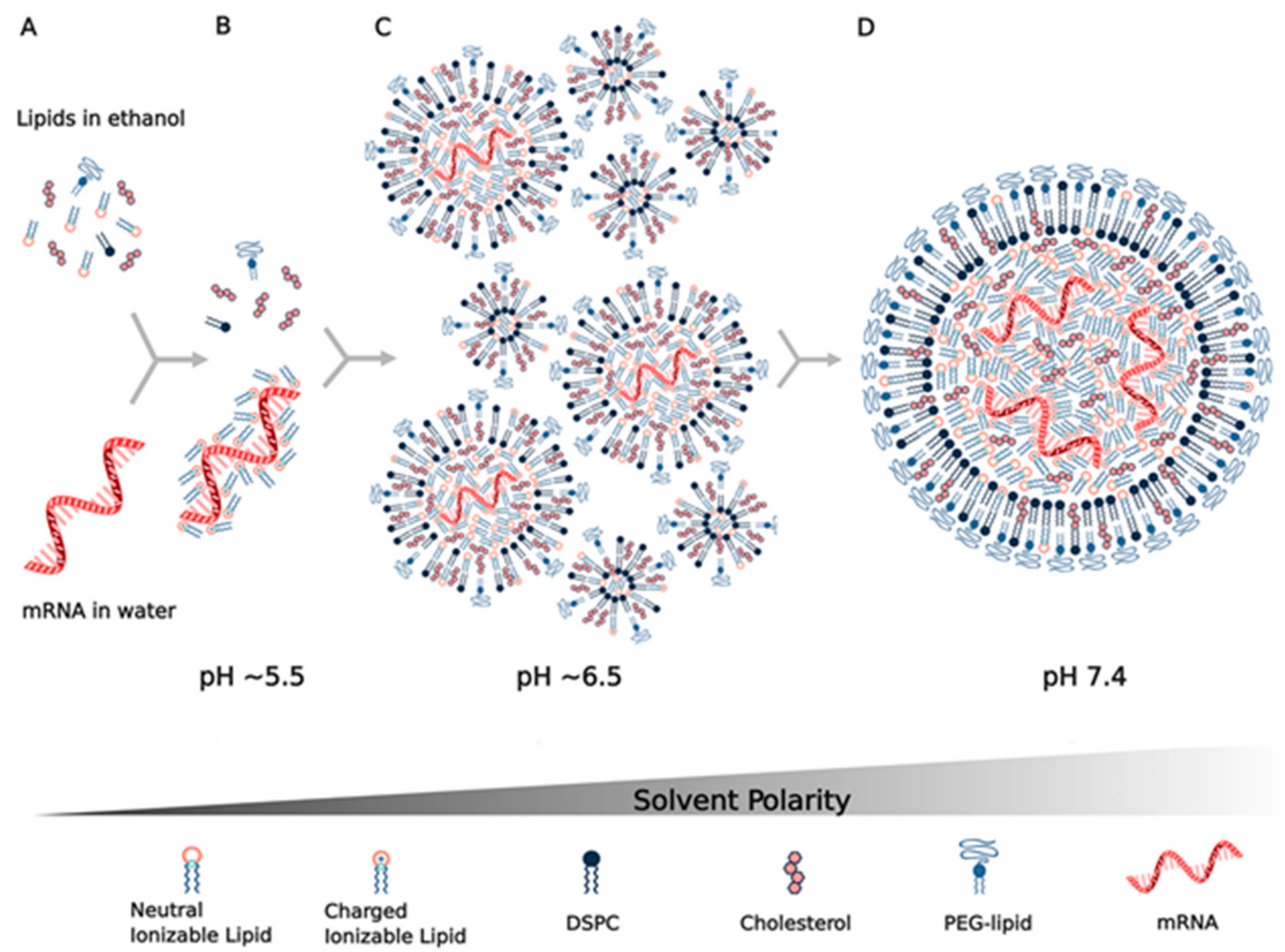
Vaccines Free Full Text Nanomaterial Delivery Systems For Mrna Vaccines Html